Navigating GST/HST: A simplified guide for Canadian businesses
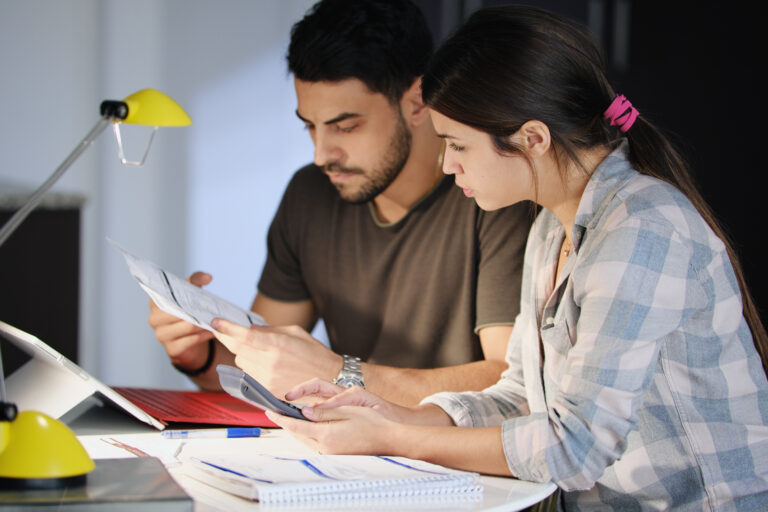
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) framework can be a labyrinth for some people. If you are struggling with this or just want to know more about the topic, by reading this concise guide you will understand all you need to know about the GST/HST.
These are essential components of Canada’s tax system, and compliance is crucial for businesses. You will get clear explanations, and practical tips, to help you comply with tax obligations, make informed financial decisions, and minimize potential pitfalls related to these taxes. Whether you’re a small start-up or an established enterprise, this guide can be a valuable tool to ensure smooth tax operations.
Understanding GST / HST Basics
In the realm of Canadian taxation, the Goods and Services Tax/Harmonized Sales Tax (GST/HST) is the cornerstone of fiscal governance for businesses. Let’s take a look into the fundamental concepts of GST and HST, by breaking down their essential components.
Benefits of Incorporation for Ontario REALTORS
For a complete list of all provinces Click Here
ALBERTA
GST (5%): $0.05
PST (0%): $0.00
NEW BRUNSWICK
HST: (15%)
Fed. (5%) + Prov. (10%)
BRITISH COLUMBIA
GST (5%): $0.05
PST (7%): $0.07
ONTARIO
HST: 13%
Fed. (5%) + Prov. (8%)
MANITOBA
GST (5%): $0.05
PST (7%): $0.07
SASKATCHEWAN
GST (5%): $0.05
PST (6%): $0.06
Goods and Services Tax (GST): The GST is a federal tax levied on most goods and services across Canada. It currently stands at a standard rate of 5%. This tax is a crucial source of revenue for the federal government and is collected at various stages of the supply chain.
Harmonized Sales Tax (HST): In certain provinces, the GST is combined with a provincial sales tax to form the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST). The HST consolidates federal and local taxes into a single harmonized rate. It simplifies the tax collection process for businesses operating in these provinces. Currently, HST rates vary by province, ranging from 13% to 15%.
Input Tax Credits (ITCs): One key feature of the GST/HST system is the availability of Input Tax Credits (ITCs). Registered businesses can claim ITCs, which allow them to recover the GST/HST they pay on business expenses. This mechanism ensures that taxes are not levied on taxes and promotes fairness in the taxation of goods and services.
Place of Supply Rules: Understanding the “place of supply” rules is critical for businesses operating in multiple provinces or dealing with international clients. These rules determine which tax rate (GST or HST) applies to a particular transaction based on the location of the recipient or the nature of the goods and services provided.
GST/HST Registration Threshold: Businesses need to be aware of the registration threshold. If your business surpasses the specified threshold for annual revenue, you are required to register for GST/HST. However, even businesses below this threshold can opt for voluntary registration to benefit from input tax credits.
Taxable and Zero-Rated Supplies: It’s vital to distinguish between taxable and zero-rated supplies. While GST/HST is applied to taxable supplies, zero-rated supplies are subject to a 0% tax rate. Understanding which category your products or services fall into can significantly impact your tax obligations and pricing strategies.
By grasping these fundamental aspects of GST and HST, businesses can lay a solid foundation for navigating Canada’s taxation landscape. In the subsequent sections of this guide, we will explore the intricacies of GST/HST further, equipping you with the knowledge needed to manage your tax responsibilities effectively.
Who Needs to Register for GST/HST?
Mandatory Registration:
The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) mandates GST/HST registration for businesses that meet specific revenue thresholds. As of our last update in September 2021, businesses with annual taxable revenues exceeding $30,000 must register for GST/HST. However, in provinces with HST, such as Ontario or British Columbia, the threshold may differ due to the combined federal and provincial tax.
Voluntary Registration:
Even if your business falls below the mandatory registration threshold, you can opt for voluntary registration. Voluntary registration has its advantages, particularly when it comes to claiming Input Tax Credits (ITCs). By voluntarily registering, you can recover the GST/HST paid on business expenses, potentially reducing your tax liability.
Benefits of Voluntary Registration:
- ITC Claiming: Voluntarily registered businesses can claim Input Tax Credits, which can lead to significant cost savings.
- Credibility: GST/HST registration can enhance your business’s credibility, mainly when dealing with larger clients or partners.
- Cross-Border Trade: If your business engages in cross-border transactions, GST/HST registration may be necessary for certain customs and tax benefits.
Considerations Before Registering: Before deciding to register for GST/HST, carefully consider factors such as your revenue, the types of customers you serve, and the impact on your pricing strategy. While registration can provide benefits, it also entails ongoing tax collection, filing, and remittance responsibilities.
Registered businesses are required to collect GST/HST from their customers on taxable supplies and subsequently remit the collected taxes to the government. Ensuring compliance with these collection and remittance obligations is critical.
GST/HST filing frequency varies depending on your annual revenue and the reporting period. Understanding the filing requirements and deadlines is crucial to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Some businesses may fall under exceptions or special cases, such as small suppliers or certain non-profit organizations. It’s essential to be aware of these exceptions and how they may affect your registration status.
Whether you are mandated to register or considering voluntary registration, understanding the implications and responsibilities is a critical step in managing your tax obligations effectively, if you have any questions about personal or business tax consultation in Mississauga you can book a call with us.
GST/HST Rates and Exemptions
After deciding on the registration, you have to be aware of the diverse tax rates and exemptions that apply across provinces. In this section, you will be provided with insights about the variations in GST and HST rates and explore common exemptions.
GST Rates by Province: As of our last update in September 2021, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) maintains a uniform federal rate of 5% across all provinces in Canada. This rate applies to most goods and services unless specifically exempted.
Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) Rates: In contrast, provinces participating in the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) system combine the federal GST with a provincial component. HST rates vary by province and range from 13% to 15%. Notable HST provinces include Ontario, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador.
Provincial Sales Tax (PST): Some provinces have opted to retain their Provincial Sales Tax (PST) separately from the GST. These provinces include British Columbia, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba.
Zero-Rated and Exempt Supplies: While most supplies are subject to GST or HST, certain categories fall into either zero-rated or exempt status. Zero-rated supplies are taxable at a 0% rate, meaning no tax is collected, but businesses can still claim Input Tax Credits (ITCs). Exempt supplies, on the other hand, are not subject to GST/HST, and ITCs cannot be claimed for related expenses.
Common Exemptions: Exemptions under GST/HST often apply to essential goods and services such as healthcare, education, childcare, and financial services. Businesses must identify whether their offerings fall into an exempt category, as this can impact pricing and tax obligations.
Correctly determining the applicable tax rate (GST or HST) for your transactions is typically based on the location of your customer and the nature of the supplies provided. Understanding the “place of supply” rules is key in this regard.
It’s important to stay informed about potential changes in GST/HST rates, as these can impact your business’s tax liability. Rates may be subject to revision by federal and provincial authorities.
Businesses must charge the correct tax and manage their Input Tax Credits (ITCs) effectively to optimize their financial position.
Common GST/HST Mistakes to Avoid
As it was said before, Canadian taxation overall might seem complicated sometimes, so now that you have a clear perspective of what to do, you also need to know what you need to avoid. In this section, you will identify some common mistakes and how to steer clear of them.
- a) Incorrect Tax Rates: One of the most common errors is applying the wrong GST/HST rate to a transaction. Ensure you understand the tax rates applicable to your location and the nature of your supplies. Keep abreast of any rate changes that may occur over time.
- b) Filing Errors: Filing mistakes, such as reporting incorrect figures or missing filing deadlines, can lead to penalties and interest charges. Implement robust record-keeping practices, use online filing options, and double-check your returns for accuracy.
- c) Missing Input Tax Credits (ITCs): Failing to claim all eligible Input Tax Credits (ITCs) can result in paying more GST/HST than necessary. Maintain meticulous records of your expenses, categorize them correctly, and claim ITCs for all applicable purchases.
- d) Incomplete Invoices: Inadequate invoicing can lead to compliance issues. Ensure that your invoices contain all required information, including your business name, GST/HST registration number, description of supplies, and the applicable tax rate.
- e) Improper Documentation: Poor record-keeping can be a costly mistake. Keep organized records of invoices, receipts, and financial transactions related to GST/HST. Accurate documentation is essential for audit purposes and verifying ITC claims.
- f) Late Remittance: Missing deadlines for remitting collected GST/HST can result in penalties and interest charges. Keep a close eye on remittance due dates and choose a convenient payment method to ensure timely payments.
- g) Ignoring Place of Supply Rules: Neglecting the “place of supply” rules can lead to charging the wrong tax rate on transactions. Be aware of the rules that determine whether GST or HST applies, depending on the location of your customer and the nature of the supplies.
- h) Neglecting Voluntary Disclosure: Businesses often hesitate to make voluntary disclosures when errors are discovered. However, this can be a costly omission. If you identify errors or omissions in your past filings, consider making a voluntary disclosure to rectify them and minimize penalties.
- i) Inadequate Training and Knowledge: Insufficient training and knowledge of GST/HST regulations can lead to compliance errors. Invest in education and training for yourself and your staff to ensure a thorough understanding of tax obligations.
- j) Lack of Regular Updates: Tax regulations and rates may change over time. Failing to stay informed about updates can result in outdated practices that lead to errors. Regularly check for updates from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) to stay current.
- k) Overlooking Exemptions: Not recognizing exemptions for specific goods or services can lead to overcharging customers and potentially damaging your reputation. Be aware of the categories that qualify for exemptions and apply them correctly.
As you move forward, we encourage you to take informed action. Stay vigilant in calculating and collecting the correct tax rates, maintain meticulous records, and adhere to filing deadlines. Embrace technology and online resources to streamline your tax management processes. In cases of errors or omissions, consider the option of making voluntary disclosures to rectify them.
Remember that GST/HST compliance is not solely a financial obligation; it’s a commitment to the integrity and credibility of your business. Accurate tax management not only prevents penalties but also builds trust with customers, partners, and tax authorities.
We understand that the world of taxation is ever-evolving, and regulations may change. Therefore, we encourage you to stay informed about updates from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) and seek professional advice when needed. Don’t forget each person or business has different needs, for any tax consulting services in Mississauga or anywhere else, we can help you.
For a free no-obligation consultation, please contact us at (647) 484-0909
KPAG Consulting